Impacts of Electric Vehicle on Power System
Electric vehicles (EVs) have been gaining popularity in recent years as a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. In India, EV sales have grown by 148% compared to the previous year, with the government aiming for EVs to account for 30% of private cars, 70% of commercial vehicles, and 80% of 2W and 3W by 2030. However, this rapid growth in EVs has raised concerns about the impact on the power grid, which must provide the necessary electricity to charge the vehicles. In this article, we will explore the challenges posed by EVs to power grids and the solutions to address them.
Challenges Posed by EVs to Power Grids
EVs consume a large amount of electricity to charge their batteries, and this can pose several challenges to power grids.
Voltage Instability and Phase Unbalance
EVs consume a significant amount of power in a short time to charge their batteries, which can cause voltage instability and phase unbalance in the distribution network. This can have negative effects on the operation of the network and connected loads, especially in rural areas where voltage drops are more common.
Overloading of Distribution Network Components
The high demand for electricity to charge EVs can overload distribution network components such as transformers and cables, which may not be designed to handle such loads. This problem is exacerbated by fast charging, which puts even more strain on the distribution network.
Harmonics Distortion
EV integration can cause harmonics distortion, which is the generation of frequencies other than the fundamental frequency of 50Hz. This can cause power loss and result in overheating of transformers and cables, reducing their lifespan.
Solutions to Address the Impact of EVs on Power Grids
Proper charging algorithms and the integration of renewable energy sources are two solutions to address the impact of EVs on power grids.sing Proper Charging Algorithms
Using Proper Charging Algorithms
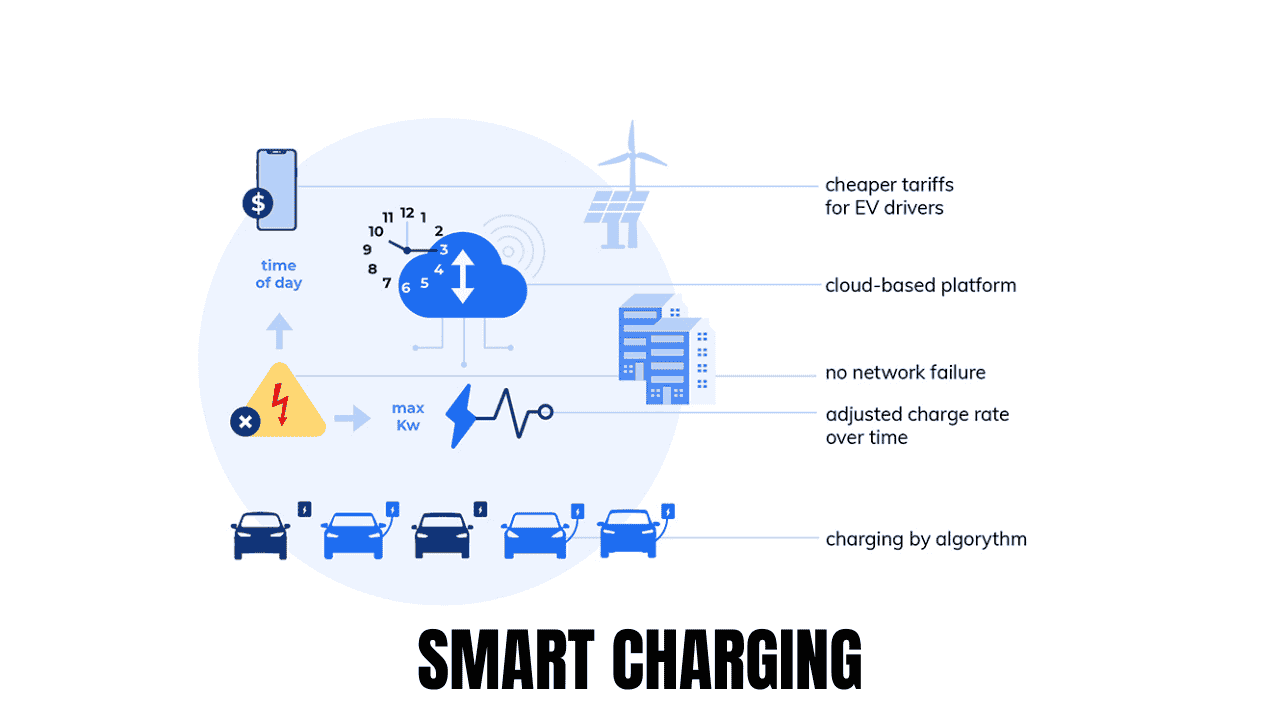
Smart Charging and Delayed Charging algorithms can be used to minimize the impact of EVs on power grids. Smart Charging communicates between power distributor & charging stations or points to charge EVs when the load on grid is less. It also discharges the battery to send power back to the grid when demand is at its peak. This is a concept known as Vehicle to Grid (V2G). Smart Charging flattens the load curve and increases the lifespan of power distribution components such as transformers and cables, but it is costly to implement due to its complexity and communication protocols.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy, when integrated into charging stations, can make the power supply more reliable & reduce the burden on the power grid. This integration can be achieved through micro-grids that can operate independently or in conjunction with the power grid.
Conclusion
The rapid growth of EVs in India presents several challenges to the power grid, including voltage instability and phase unbalance. Also overloading of distribution network components, and harmonics distortion. These challenges can be addressed by using proper charging algorithms. Like Smart Charging and Delayed Charging, and integrating renewable energy sources such as solar and wind energy. These solutions can not only minimize the negative impacts of EVs on the power grid. But also contribute to a more sustainable and reliable energy future. To know more about electric vehicle in India you can follow EcoVahan.com.

